Biomedical research and services
Avantea’s biomedical research uses advanced animal models to study human diseases, test drugs and develop new therapies. Using reproductive biotechnology and genetic engineering technologies, this research enables the reproduction of human pathologies on animal models, enabling scientists to better understand the mechanisms of diseases and develop innovative cures.
Objectives of biomedical research
Understand
human diseases
Develops animal models that reproduce genetic, neurodegenerative and cardiovascular conditions.
Contributing to progress of transplantation
Advanced xenotransplantation studies for develop human-compatible organs.
Develop new therapies and drugs
Testing of innovative treatments before clinical trials to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Improving regenerative medicine
Study the potential of stem cells to repair damaged organs and tissues.
Reducing the use of animals in experiments
Development of in vitro tests and alternative methodologies for toxicological evaluation.
Animal models for
medical research
Animal models allow the mechanisms of disease to be analysed, new drugs to be tested and innovative treatments to be developed in a controlled environment.
Animal models are organisms used in scientific research to reproduce human diseases, allowing us to study their development and identify possible cures.
Objective
Create animal models that reproduce human diseases to study therapies and treatments.
Method
Genetic modification of pigs to simulate complex pathologies such as neurodegenerative or cardiovascular diseases.
Examples of application
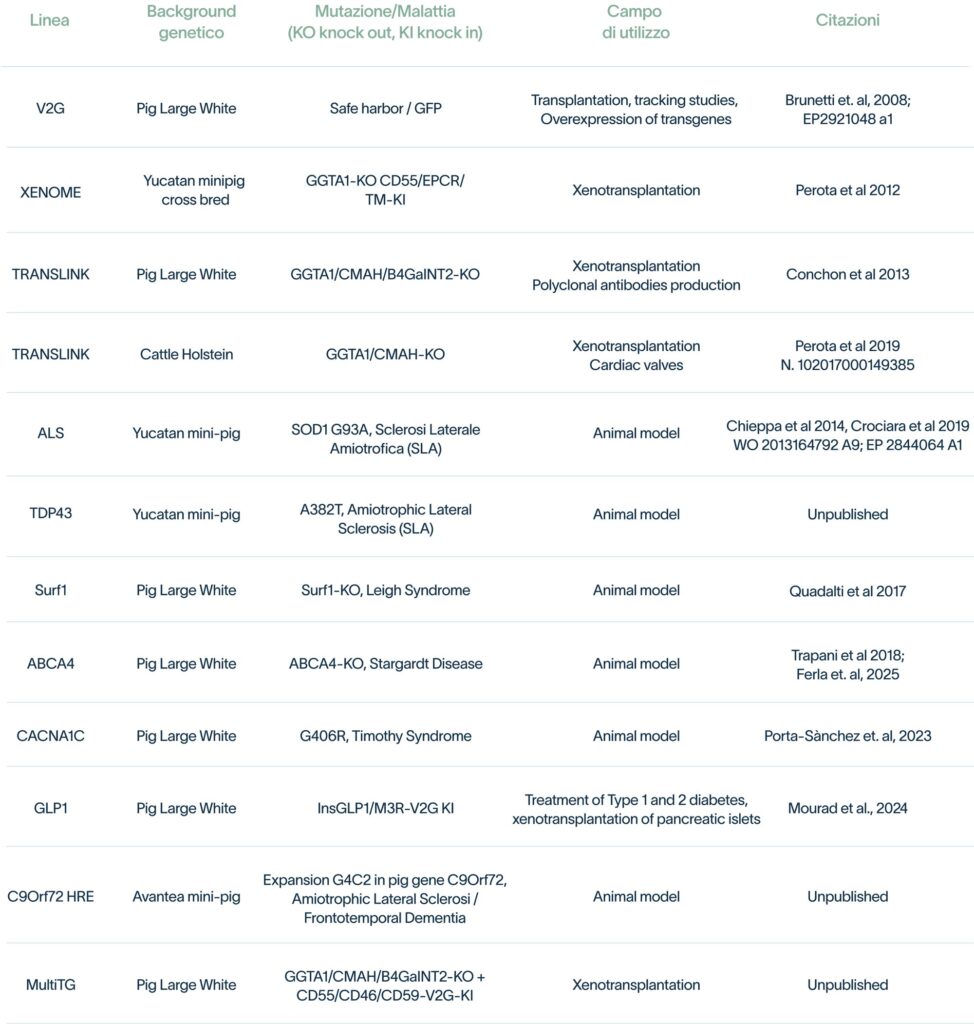
- Human genetic disease models → Pigs are genetically modified to reproduce rare and complex human diseases, such as ALS, Leigh’s syndrome or muscular dystrophy, allowing researchers to study the mechanisms of the disease and test possible therapies.
- Xenotransplantation Study → and development of organs and animal tissues compatible for human transplantation, with the goal of reducing the donor shortage. Through the genetic modification of pigs, work is being done to make their organs more compatible with the human immune system, lowering the risk of rejection and opening new possibilities in transplant medicine.
Why is it important?
Pigs have a physiology very similar to that of humans,
making them ideal models for testing new treatments
before clinical trials.
Models Animals
Development of genetically modified pig models to simulate Human diseases, allowing the study of genetic diseases rare, neurodegenerative disorders and new medical therapies.
Xenotransplantation
Develop compatible organs and tissues for inter-species transplantation, offering solutions to the shortage of human donor organs.
In vitro toxicity test
An ethical alternative to animal testing
Toxicity tests are scientific analyses used to assess the effects of drugs, chemicals and cosmetics on the human body. Traditionally performed on animals, these tests can now be conducted in vitro using human cells grown in the laboratory.
This approach allows for the precise study of the toxic effects of substances, ensuring a more reliable assessment and reducing the use of animal testing.
Objective
Assess the safety of drugs, cosmetics and chemicals without using laboratory animals.
Method
Use of human cells cultured in the laboratory to test the effects of substances.
Examples of application
- Reproductive toxicity test → Analysis of the effect of
fertility drugs and chemicals. - Cosmetic industry → Verification of non-toxic effects on beauty products.
- Biomedical materials → Biocompatibility tests of medical devices.
- Pharmaceutical field → Testing of new molecules
before the clinical trial.
Why is it important?
In vitro tests provide more accurate data and reduce
the use of animals in research.
Toxicity tests
Safety assessment of drugs, cosmetics, and substances using in vitro tests based on stem cells and bovine embryo models, avoiding traditional animal testing and ensuring more predictive results for human health.
Stem cells and regenerative medicine
Stem cells are unique cells that can transform into different types of cells in the human body.
Their ability to differentiate makes them fundamental for medical research and the development of new therapies.
Objective
Studying the potential of stem cells to regenerate tissues and treat degenerative diseases.
Method
Cell culture and differentiation of stem cells to understand their use in cell therapy.
Examples of application
- Regenerative medicine → Study of the repair of
damaged tissues, such as the heart or spinal cord
Why is it important?
Stem cells can revolutionise the treatment of many diseases that are now incurable.
